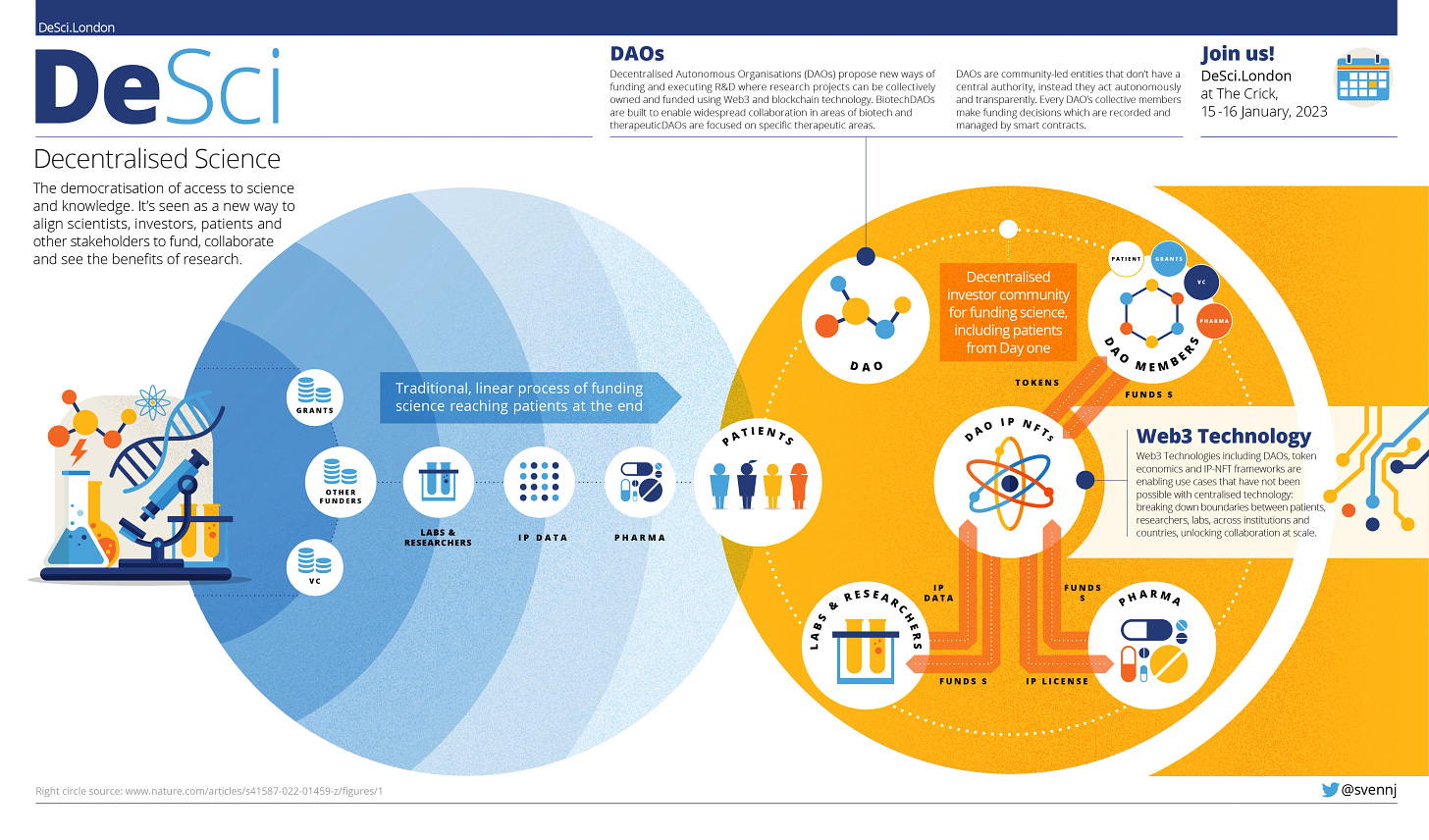
Is Decentralised Science better science?
DeSci is tackling all the big problems in science: funding, data access, IP and more. Some DeSci organisations have already taken hold, but the more radical initiatives are still in the early stages.
Between publish or perish mentality, academic paywalls and funding challenges, researchers operate under an imposing structure of limitations and rules. Changing the overall system in order to overcome these issues and enable scientific research to flourish unbounded is an intimidating task. But that’s exactly what decentralised science (DeSci) aims to do.
DeSci aims to radically transform the very way science gets done by replacing publishers with crowdsourcing, making datasets open-source, and relying on decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs) to support the process — among various other improvements.
Here, we’ll dive into what DeSci means, how it may support better science, and what initiatives are already operating under this new paradigm.
“DeSci offers the potential to radically alter how a new generation of great minds are incentivized to tackle major scientific and technological challenges” - Joseph Cook, Glaciologist
What is DeSci?
Decentralised science refers to the mission to shift resources and influence from centralised sources like publishers and academic institutions (and other profit-focused entities) to researchers themselves. The concept is tightly connected to a variety of other “open research” initiatives, like open-access for research papers (see our article on how open access impacts research) and ensuring open-access for datasets. Per its name, DeSci calls upon a variety of decentralised tools and structural changes including reliance on the blockchain and new funding paradigms like quadratic funding and crowdsourcing.
In short, DeSci seeks to overcome existing issues in the scientific sphere by optimising the funding, distribution and execution of research using blockchain technology.
The connection between DeSci and blockchain
At their core, all DeSci solutions rely on blockchain technologies to function. These form the fundamental decentralised nature of the approach.
Although the underlying tech is roughly the same, there are various ways it can can be applied to the academic infrastructure, whether as a means of publishing papers, evaluating researchers or managing funds. Here are a few ways blockchain technology may be, or already is, used to support DeSci:
Change how we evaluate academic achievement by replacing traditional values like h-index with token recognition systems that run on blockchain
Make it easier for scientists to reproduce existing studies. For example, by keeping track of data better or storing metadata on the blockchain.
DeSci DAOs, which connect funds to researchers, run on blockchain technology. These include organisations like SCINET (life sciences), Antidote DAO (cancer research), AthenaDAO (women’s health), Cherubs DAO (Alzheimer’s and brain health), Frontier DAO (climate and space), and PsyDAO (psychedelics and mental health), just to name a few.
Other decentralised research funding platforms also use blockchain, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and/or Web3 technologies, like Science Fund and DEIP. Science Fund uses smart contracts and a custom NFT called Science Funding Token (SFT) to keep track of and award research-related content to donors.
Does DeSci make for better science?
The current paradigm of scientific research — whether in academia or industry — suffers from a variety of significant issues and drawbacks. These range from challenges with publishing (excessive costs) to researchers losing time writing grant proposals to just basic reproducibility issues. Decentralised science initiatives address these and other issues using blockchain technology, to democratise and automate more of the research process.
Here are several commonly cited issues and their “DeSci solutions”:
Funding amount: Instead of a small group of people controlling funds (review boards, etc.), distribute funds through DAOs, quadratic funding, crowdfunding, and tokenised recognition systems
Funding time: Instead of making researchers wait months or years to hear back about funding decisions, provide swift and transparent responses
Collaborations: Instead of having collaborations limited to certain people (whether by institutional limitations or just difficulty connecting) researchers can collaborate with peers from a global network
Peer review: Incentivise peer-review by having researchers earn tokens and reputation
IP: Instead of institutions and universities owning all the intellectual property of researchers, researchers own their intellectual property (IP)
Reproducibility: Make studies easier to reproduce by using DeSci methods to make reproducibility inherent in the process
DeSci clearly presents a promising set of solutions to the existing issues in the funding and execution of scientific research. It places more power in the hands of researchers, saves time, and has the potential to better connect people than the existing system. However, as we’ll discuss below, the most widely-adopted DeSci initiatives today still play into the existing system of research without altering it too heavily. The most radical changes are still yet to be seen. Although DeSci may have what it takes to solve the problems plaguing traditional research systems — particularly with respect to peer-review, funding and data availability — the degree to which it may fundamentally transform these systems yet remains unclear.
Is DeSci really transforming academic systems?
Although the broad DeSci mission is ambitious, some of the most successful DeSci initiatives thus far are often on a more localised and transitional scale. The most successful implementations so far seem to be those that integrate easily into the existing academic atmosphere.
For example, blockchain technology is being actively applied to the existing publishing paradigm, in ways that currently impact and serve researchers, publishers and universities. Take ARTiFACTS File, a blockchain-based system designed to reliably keep track of publications from participating researchers, allowing institutions to better monitor and review of the contributions of researchers. Since citations and paper publications are all recorded, university staff can use the blockchain to review and evaluate researchers.
Orvium, a CERN spin-off, has a similar idea, and aims to take on the publishing process in a way that better serves scientists, publishers, and reviewers. Both tools don’t seek to radically transform academia, but simply apply blockchain and new perspectives to the existing paradigm.
On the other hand, more radical DeSci initiatives that seek to change the way research gets done are generally still in the early stages. Predominantly, these are DAOs focused on serving the research community by making funding easier to access and connecting research more directly to the people it serves. However, DAOs aren’t without their own set of challenges.
VitaDAO, one of the best-known DAOs focusing on longevity science, openly express the fact that their company is still in the “early stages and faces financing risks if market conditions weaken”. As one dives into the world of DAOs and revolutionary blockchain startups designed for academic overhaul, it is distinctly reminiscent of the broader blockchain and NFT hype. With many DAOs still in the early stages, it’s yet unclear which will will prevail and which may struggle to be financially viable.
The downsides of decentralised science include all the risks and challenges associated with the blockchain — volatility, regulatory pressure, cyber attacks, etc. — as well as any other unexpected outcomes to the academic world. For example, in a system where all researchers openly contribute to peer-review via collaborative token-based networks, what’s the impact for existing journals? Will it compromise the relative “ranking” of journals, and what are the consequences?
The current state of DeSci
Currently, DeSci is a worldwide movement, best represented by online communities, leading foundations that advocate for it, and a diverse set of DAOs and centralised platforms.
As with most decentralised initiatives, DeSci is community-oriented, consisting of many hubs, discussion channels, and tokens. Plenty of DeSci ecosystems already exist on which researchers may conduct their research (or apply for funds). These include Web3 platforms which provide funding or even sites like ResearchHub which make research more widely available and make it easier to find collaborators.
There are various community groups, resources and organisations in the DeSci movement, some of which are listed below.
DeSci Community groups
Desci.global provides a calendar of all DeSci events across the world
DeSci thought-leaders and key foundations
DeSci Foundation is an independent organisation made up of scientists and innovators, exploring a variety of DeSci initiatives including open-science practices, FAIR data, open peer review, replication studies, fair rewards, and better funding models. They offer a high-quality blog on various topics including how Web3 can help scientists and why the current business of research journals needs to change.
DeSci World is a centralised community hub, featuring DeSci projects, events, labs, jobs and organisations.
DeSci research hubs
Bloxberg supports worldwide collaboration among researchers. It has a bold mission to advance science by providing a secure and accessible infrastructure. Bloxberg has a host of collaborators and tools, such as SAIRA, which allows researchers to find, join and manage research collaborations.
ResearchHub aims to help scientists collaborate better by eliminating inefficiencies and incentivising collaboration via their reward token ResearchCoin (RSC). They have a community Discord, too. Any researcher can join ResearchHub and begin engaging in conversations with peers.
DeSci-focused computational resources and data
LabDAO — focused on the life sciences — aims to provide the research community funding, collaborators, and, perhaps most critically, generous resources like one petabyte of cloud storage and distributed compute infrastructure. LabDAO received recent attention from its presentation at a Blockchain Meets Biology summit in April, but is still building out its platform.
dClimate provides free climate data
Environmental Data Initiative (EDI) serves to make all environmental and ecological data Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR), and recently had a ten-year review paper on its work. Although EDI isn’t technically part of the DeSci movement (it doesn’t run on blockchain and is governmentally funded) it’s still a great resource for free, FAIR ecological data.
Active Inference Institute is a DeSci initiative focused on the particular domain of active inference — a way of understanding sentient behaviour. They use the DeSci model to make available their cognitive models and community resources.
DeSci organisations for biomedical and life sciences
Molecule aims to be a funding ecosystem for early-stage biotech and medical research discoveries. They’ve already funded projects via DAOs like The Longevity Molecule, focused on the research of ageing.
VitaDAO is a decentralised autonomous organisation that funds longevity science, and has already invested $4 million in projects.
Fleming Protocol is a still in-progress initiative to create an open-source data economy for biomedical research, enabling patients to work directly with labs.
Bio.xyz is focused on funding biotech science through its community of DAOs.
CureDAO seeks to overcome the existing economic system in biomedical research by using decentralised strategies in order to support meaningful health research.
SCINET allows institutional investors to invest straight into researchers, but is still in its early stages.
AthenaDAO accepts project submissions for research pertaining to women’s health, with grants ranging from $50-150K, motivated by the fact that women’s health research is traditionally under-funded.
DeSci funding platforms
Science Fund is a Web3 tool that keeps track of the scientific impact of research in order to effectively fund new research through NFTs.
Gitcoin is a general Web3 funding platform, but with its focus on public good is appropriate as a funding venue for some researchers.
Longevity Decentralized Review provides funds for scientists to review each other’s work in longevity research — particularly preprints.
Today’s bottom line on DeSci
DeSci is an ambitious mission to transform how scientific research gets done. Although many organisations have sprung up in the last few years under the DeSci banner, most are still in the early stages. The largest organisations to-date feature decentralised technology tend to be those which integrate into the existing academic paradigm, whereas the more radical organisations trying to create Web3 marketplaces and the like are still being developed.
Although DeSci resolves to fix existing issues in the traditional scientific process, it also comes with its own set of challenges. It carries the same risks associated with blockchain technology, like the volatility and potential for cyber attacks. Although many DAOs are popping up, eager to fund scientific ventures, its yet unclear which ones will be financially viable in the long-term. Much remains to be seen for what the trajectory DeSci initiatives will look like and how much flexibility existing institutions have to handle the more radical approaches.
Do you think DeSci means for a better scientific future? Tell us what you think by commenting below or tweeting at us @LitmapsApp!
Resources
Science 37 : The Time for Decentralized Clinical Trials is Now, May 2023
Decentralized Clinical Trials for Drugs, Biological Products, and Devices by the FDA, May 2023
The DeSci Movement: Will Crypto Really Solve Science's Biggest Problems?, April 2023
Decentralized science is key to fixing academic research, April 2023
What is DeSci?, February 2023
Unblocking recognition: A token system for acknowledging academic contribution, February 2023
Understanding science funding in tech, 2011-2021, March 2022
A Guide to DeSci, the Latest Web3 Movement, February 2022
What is decentralized science (DeSci)?, from Ethereum
Blockchain For Science, journal venue